1. Overview
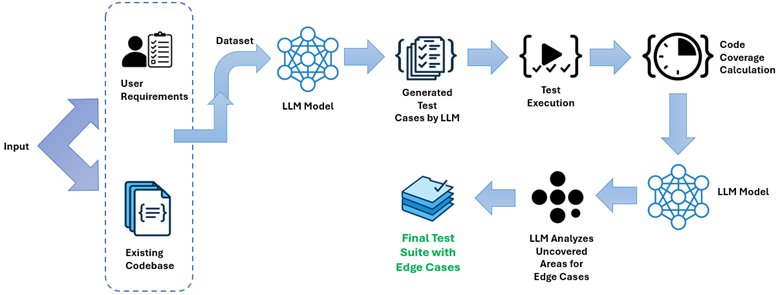
Software testing remains a critical stage in the software development lifecycle, ensuring correctness, reliability, and robustness across diverse execution conditions. Traditional testing approaches require extensive manual effort, which leads to incomplete coverage and overlooked edge cases. The emergence of Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) has significantly improved automated test creation, helping developers generate test cases with high code coverage, better path exploration, and stronger edge-case detection.
Recent work demonstrates that LLMs can produce high-accuracy test suites, generate complex edge-case inputs, and accelerate test development. For example, LLM-based test automation achieved up to 100% code coverage and consistent detection of at least one edge case per function in controlled experiments [1].
Meanwhile, new research benchmarks such as TESTEVAL show that LLMs can generate highly diverse tests, though targeted branch/path exploration remains challenging [2]. Another major innovation, mutation-guided LLM test generation, improves fault detection significantly by prompting the model with surviving mutants [3].
2. How Generative AI Improves Test Quality
2.1 Automated High-Coverage Test Generation
Generative AI can automate the production of unit tests, mocks, assertions, regression scenarios, and even complex boundary inputs. Studies show GPT-4 can generate high-quality pytest cases with:
High executability, High functional correctness, Up to 100% code coverage, Automatic identification of multiple edge cases [1].
2.2 Coverage-Targeted Test Generation
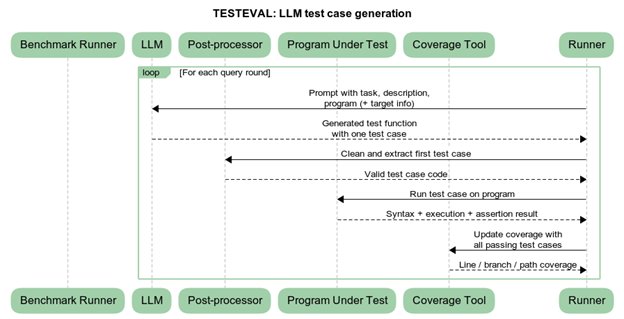
The TESTEVAL benchmark evaluates LLMs on three dimensions:
(1) Overall line/branch coverage, (2) Target-line or target-branch coverage, (3) Target-path coverage.
Results indicate that although state-of-the-art LLMs such as GPT-4o achieve 98.65% line coverage and 97.16% branch coverage, they still face difficulty generating tests for specific lines or execution paths [2].
2.3 Mutation-Guided Quality Improvement
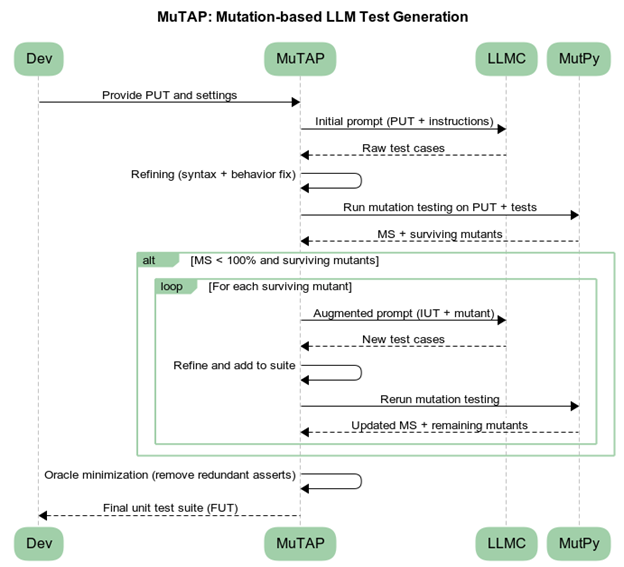
MuTAP is a technique that uses mutation testing to improve bug-revealing capability by supplying surviving mutants as an additional prompt context. Their findings show:
- Up to 28% more real bugs detected
- 17% more bugs detected than both Pynguin and few-shot LLM baselines
- 57% mutation score, dramatically higher than traditional generators
[3]
This demonstrates that mutation-guided prompting is a breakthrough technique for improving test effectiveness.
3. Key Research Themes
3.1 Code Coverage ≠ Test Effectiveness
Research consistently shows that code coverage alone is not enough. High coverage can still miss critical faults, and LLMs may generate many lines of trivial coverage without meaningful assertions [3] .
3.2 Edge-Case Sensitivity
LLMs can identify missing corner cases such as Empty lists, Very large numbers, Negative values, Mismatched types, Rare boolean combinations.
The Genç (2025) study reports that every function received at least one LLM-generated edge case [1].
3.3 Diversity of Test Cases
TESTEVAL introduced cov@k, a diversity metric showing how well a small subset of generated tests covers program logic [2]. Higher diversity indicates more meaningful test exploration.
3.4 Mutation-Driven Test Refinement
MuTAP’s augmentation pipeline:
- Generate initial tests
- Run mutation testing
- Identify surviving mutants
- Re-prompt LLM with mutants
- Produce refined tests with stronger assertions
This significantly improves bug-revealing power [3].
4. Tools and Technologies
Tool name | Functionality | Advantage | Source |
TESTEVAL | Benchmark for LLM-generated tests | Enables objective comparison of LLM test quality | [2] |
MuTAP | LLM test generation with mutation feedback | Improves tests by iterating on mutation results | [3]
|
Pynguin | Python automated unit test generator | Automatically creates unit tests for Python code | [4]
|
EvoSuite | Search-based Java test generation | Uses search algorithms to maximize coverage | [5]
|
GitHub Copilot Tests | In-IDE auto-generation of unit/integration tests | Speeds up test creation inside common editors | [6]
|
OpenAI GPT-4o Testing Workflows | Test design and script drafting from specs | Flexible, model-driven test planning and authoring | [7]
|
testRigor AI Testing | No-code English-based E2E and API tests | Lets non-devs build robust tests quickly | [8]
|
Diffblue Cover (Java) | Autonomous Java unit test generator | Rapidly increases and maintains Java test coverage | [9]
|
Codeium Test Suggestions | IDE test and edge-case suggestions | Integrates test ideas directly into coding flow | [10]
|
Harness Test Intelligence AI | AI-driven test creation and self-healing | Optimizes CI/CD testing with resilient test suites | [11]
|
5. Limitations of GenAI in Testing
Even though LLMs are powerful, several limitations remain:
- LLMs sometimes hallucinate expected outputs, requiring correction via post-processing steps like intended behavior repair [3] .
- TESTEVAL shows LLMs struggle to generate tests that reliably hit specific branches or complex paths [2] .
- LLMs may generate high-coverage but low-quality tests lacking meaningful oracle checks.
6. Future Research Directions
- Hybrid Symbolic Execution + LLMs: Combining the reasoning of solvers with LLM creativity.
- Multi-Agent AI Testing Systems: Specialized agents for Fuzzing, Branch/path, coverage, Mutation optimization, Oracle repair.
- Program-Comprehension-Aware LLMs: Models explicitly trained for program structure and semantics (AST, CFG, SSA).
- Mutation-Driven Benchmarks: Making mutation score a first-class evaluation metric.
7. Conclusion
Generative AI has transformed automated software testing. Current research demonstrates:
- Near-perfect coverage (98–100%)
- Effective automatic edge-case detection
- Dramatic improvements in bug-revealing power through mutation-guided prompting
However, high coverage alone is insufficient. The field is transitioning toward holistic test quality metrics that include coverage, edge-case diversity, and mutation score. With the synergy of LLM reasoning, benchmark frameworks, and mutation-aware pipelines, the next generation of automated testing will be significantly more intelligent, adaptive, and reliable.
References
[1] Genç, S., Ceylan, M. F., & İstanbullu, A. (2025, September). Software Unit Test Automation with LLM-Based Generative AI: Evaluating Test Quality through Code Coverage and Edge-Case Analysis. In 2025 10th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK) (pp. 242-247). IEEE.
[2] Wang, W., Yang, C., Wang, Z., Huang, Y., Chu, Z., Song, D., … & Ma, L. (2025, April). Testeval: Benchmarking large language models for test case generation. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2025 (pp. 3547-3562).
[3] Dakhel, A. M., Nikanjam, A., Majdinasab, V., Khomh, F., & Desmarais, M. C. (2024). Effective test generation using pre-trained large language models and mutation testing. Information and Software Technology, 171, 107468.
[4] Fraser, G., & Arcuri, A. (2011, September). Evosuite: automatic test suite generation for object-oriented software. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGSOFT symposium and the 13th European conference on Foundations of software engineering (pp. 416-419).
[5] Lukasczyk, S., & Fraser, G. (2022, May). Pynguin: Automated unit test generation for python. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings (pp. 168-172).
[6] https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/copilot/guides/test-with-copilot
[7] https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/reasoning-best-practices
[8] https://testrigor.com
[9] https://www.diffblue.com
[10] https://codeium.com
[11] https://www.harness.io/products/ai-test-automation

